Describes the Formation of Eukaryotic Cells
Eukaryotic cells Essays. The endosymbiotic hypothesis for the origin of the eukaryotic cell has been applied to the origin of the mitochondria and chloroplasts.

Tj Dna Molecules Can Coil And Bend In Space Leading To Changes In Topology Including Formation Of Negative Or P Dna Replication Dna Molecule Eukaryotic Cell
S phase is the period during which DNA replication occurs.

. Order 1 G1 Phase Chromosomes and centrioles are duplicated. Beyond the structure of DNA eukaryotic cell organelles are formed from pre-existing organelles dividing by fission to multiply like a bacteria. Because a membrane surrounds eukaryotic cells nucleus it has a true nucleus.
It is composed of a ring of protein tubes called microtubules which are also part of the cytoskeleton. Compare and contrast the life cycles of each of the cells. The most important distinguishing factor between eukaryotic and bacterial cells is the presence and absence of the nucleus respectively.
Identify any advantages or disadvantages of each of the organisms. 1 a membrane-bound nucleus. However unlike prokaryotic cells eukaryotic cells have.
Discuss composition of each of the cellular structures and what their molecules are used for. The nuclear genome of eukaryotes is related most closely to the Archaea so it may have been an early archaean that engulfed a bacterial cell that evolved into a mitochondrion. Skin cell This stage varies in length and can last for minutes or years.
The centrosome directs the formation of the spindle involved in cell division. In bacterial cells the genetic material is arranged in a circular material called a nucleoid. In multicellular eukaryotic organisms the production of new cells follows a highly regulated sequence of growth DNA replication and division.
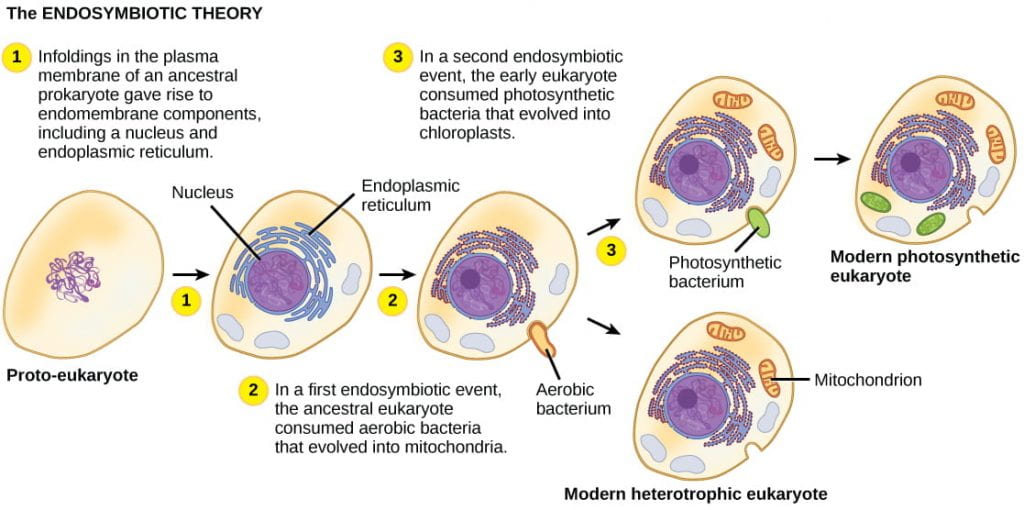
Within each eukaryotic cell internal membranes create multiple compartments. The hydrogen hypothesis holds that eukaryotic cells originated through a symbiotic metabolic association in anaerobic environments between a fermentive α-proteobacterium that generated hydrogen and CO 2 as waste products and a strict anaerobic autotrophic archaeon that depended on hydrogen and might have been a methanogen. Unlike prokaryotic cells eukaryotic cells have.
M G1 S and G2. However as has been pointed out by Mereschowsky in 1905 it should also be applied to the nucleus as well. The endosymbiotic theory of the origin of eukaryotic cells states that all the individuals are evolved from the same individual.
Order 4a Prophase Microtubules attach to sister chromatids at their centromeres. Numerous membrane-bound organelles including the endoplasmic reticulum Golgi apparatus chloroplasts and mitochondria several rod-shaped chromosomes. Order 2 S Phase This is the last stage of interphase.
And 3 several rod-shaped chromosomes. Like a prokaryotic cell a eukaryotic cell has a plasma membrane cytoplasm and ribosomes. In accordance with the endosymbiotic theory of origin of eukaryotic cells the eukaryotes have evolved from number of cells that happened to join together and form a single eukaryotic cell.
The centrosome directs the formation of the spindle involved in cell division. The division cycle of most eukaryotic cells is divided into four discrete phases. Eukaryotic cells have greater mass than prokaryotic cells and have far more internal complexity.
Mitosis is used to produce new body cells for growth and healing while meiosis is used to produce sex cells eggs and sperm. There are two types of cells the eukaryotic cells eu means true karyo means nucleus these cells have a membrane-enclosed nucleus and there is the prokaryotic cells pro means before these are the primitive cells and do not have a nucleus these. Describe the the life cycle of a viral cell.
This sequence is referred to as the cell ___________ which consists of the G1 S G2 and M phases. Determine the type of microbe when given a description of a newly discovered microbe. Eukaryotic cells Essays.
Eukaryote cells arose through endosymbiotic events that gave rise to energy-producing organelles within the eukaryotic cells such as mitochondria and plastids. Eukaryotes include plants animals fungi and protists. Read about Eukaryotic and Viral cells and their life cycle in your textbook.
Eukaryotes are cells categorized as having a nucleus and a variety of other membrane-enclosed organelles. There is no membrane covering the genetic material so we can say that it practically floats in the cytoplasm of. 2 numerous membrane-bound organelles such as the endoplasmic reticulum Golgi apparatus chloroplasts mitochondria and others.
Order 3 G2 Phase Sister chromatids begin to condense. And eukaryotic cells 1. It is composed of a ring of protein tubes called microtubules which are also part of the cytoskeleton.
Meiosis will be discussed in a later chapter. The cell grows more The duration of these cell cycle phases varies considerably in different kinds of cells. Create a Venn diagram or concept map that clearly distinguishes bacterial archaeal and eukaryotic cells in terms of their genome organization organelles cell envelopes ribosome size and component molecules and cytoskeleton.
The Eukaryotic Cell Cycle Eukaryotes have two major types of cell division. If the nucleus mitochondria and chloroplasts are endosymbionts then it is likely that the organism. M phase mitosis is usually followed by cytokinesis.

Igcse Biology 3 25 Understand That Division Of A Cell By Meiosis Produces Four Cells Each With Half The Number Of Chromosomes Igcse Biology Meiosis Mitosis
Eukaryotes And Their Origins Organismal Biology

This Diagram Shows The Structures Inside A Eukaryotic Cell An Animal Cell Cell Structure Blackberry Health Benefits Complimentary Therapy
No comments for "Describes the Formation of Eukaryotic Cells"
Post a Comment